H1 指的是vite1用了些什么
cac
Command And Conquer is a JavaScript library for building CLI apps.
用它来做脚手架很方便 需要注意的是 [] 和 <> 的区别 在command里面,尖括号(angle brackets)是必传,方括号(square brackets)是可选 在option里面, 尖括号是暗示参数为 string / number,而方括号还包括 true
const { cac } = require('cac')
const cli = cac(`vite`)
cli.option('--type <type>', 'Choose a project type')
cli.option('--name [name]', 'Provide your name')
cli.command('lint <...files>', 'Lint files').action((files, options) => {
console.log(files, options)
})
// Display help message when `-h` or `--help` appears
cli.help()
// Display version number when `-v` or `--version` appears
// It's also used in help message
cli.version('0.0.0')
const parsed = cli.parse()
console.log(JSON.stringify(parsed, null, 2))
给一个对象定义属性
const defines = {
'processs.env': 'dev'
}
const w = {
test: '1'
}
Object.keys(defines).forEach((key) => {
const segs = key.split('.')
let target = w
for (let i = 0; i < segs.length; i++) {
const seg = segs[i]
if (i === segs.length - 1) {
target[seg] = defines[key]
} else {
target = target[seg] || (target[seg] = {})
}
}
})
KOA
compose
function compose (middleware) {
if (!Array.isArray(middleware)) throw new TypeError('Middleware stack must be an array!')
for (const fn of middleware) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Middleware must be composed of functions!')
}
/**
* @param {Object} context
* @return {Promise}
* @api public
*/
return function (context, next) {
// last called middleware #
let index = -1
return dispatch(0)
function dispatch (i) {
if (i <= index) return Promise.reject(new Error('next() called multiple times'))
index = i
let fn = middleware[i]
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve()
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1)))
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err)
}
}
}
}
const arr = []
const middleware = [
async (ctx, next) => {
arr.push(1)
console.log('this is 1')
await next();
arr.push(2)
},
async (ctx, next) => {
arr.push(3)
console.log('this is 2')
await next();
arr.push(4)
},
]
const fn = compose(middleware)
fn({}).then(res=>{
console.log(res,'res', arr)
// arr [1,3,4,2]
})
创建http服务
function resolveServer(
{ https = false, httpsOptions = {}, proxy }: ServerConfig,
requestListener: RequestListener
): Server {
if (!https) {
return require('http').createServer(requestListener)
}
if (proxy) {
// #484 fallback to http1 when proxy is needed.
return require('https').createServer(
resolveHttpsConfig(httpsOptions),
requestListener
)
} else {
return require('http2').createSecureServer(
{
...resolveHttpsConfig(httpsOptions),
allowHTTP1: true
},
requestListener
)
}
}
const app = new Koa<State, Context>()
const server = resolveServer(config, app.callback())
这里涉及到了node的http2服务,在node https的文档中有用到 curl命令,延申知识: curl 的用法指南 - 阮一峰的网络日志
HMR文件监听
依赖优化 optimizeDeps
node 向上查找文件
从指定目录开始向上查找指定文件列表
const fs = require('node:fs');
const path = require('node:path');
function lookupFile(
dir,
formats,
pathOnly = false
) {
for (const format of formats) {
const fullPath = path.join(dir, format)
if (fs.existsSync(fullPath) && fs.statSync(fullPath).isFile()) {
return pathOnly ? fullPath : fs.readFileSync(fullPath, 'utf-8')
}
}
const parentDir = path.dirname(dir)
if (parentDir !== dir) {
return lookupFile(parentDir, formats, pathOnly)
}
}
const pkgPath = lookupFile(root, [`package.json`], true /* pathOnly */)
缓存缓存目录
你没看错,确实是缓存缓存目录
const cacheDirCache = new Map<string, string | null>()
export function resolveOptimizedCacheDir(
root: string,
pkgPath?: string
): string | null {
const cached = cacheDirCache.get(root)
if (cached !== undefined) return cached
pkgPath = pkgPath || lookupFile(root, [`package.json`], true /* pathOnly */)
if (!pkgPath) {
return null
}
const cacheDir = path.join(path.dirname(pkgPath), OPTIMIZE_CACHE_DIR) // OPTIMIZE_CACHE_DIR: "node_modules/.vite_opt_cache"
cacheDirCache.set(root, cacheDir)
return cacheDir
}
const cacheDir = resolveOptimizedCacheDir(root, pkgPath)
// cacheDir eg.: "C:\\hemengke\\github\\vite1\\node_modules\\.vite_opt_cache"
给依赖的内容加hash
export function getDepHash(
root: string,
configPath: string | undefined
): string {
if (cachedHash) {
return cachedHash
}
let content = lookupFile(root, lockfileFormats) || ''
const pkg = JSON.parse(lookupFile(root, [`package.json`]) || '{}')
content += JSON.stringify(pkg.dependencies)
// also take config into account
if (configPath) {
content += fs.readFileSync(configPath, 'utf-8')
}
return createHash('sha1').update(content).digest('base64')
}
const depHash = getDepHash(root, config.__path)
引申内容:node 加密算法 / 编码 MD5 vs SHA-1 vs SHA-2 - Which is the Most Secure Encryption Hash and How to Check Them 如何用通俗易懂的语言解释base64? - 知乎
createHash(算法).update(内容).digest(编码)
// 用某种算法来加密某个内容然后用某种编码把加密后的内容提炼出来
node效率更高的文件操作
vite中使用fs-extra来做文件操作 fs-extra是fs的超集
await fs.remove(cacheDir)
await fs.ensureDir(cacheDir)
分析文件的import/export
- s: start
- ss: statement start
- e: end
- se: statement end
const { init, parse } = require('es-module-lexer');
(async () => {
// either await init, or call parse asynchronously
// this is necessary for the Web Assembly boot
await init;
const source = `
import a from 'a'
import b from './b'
export default a
export { b }
`
const [imports, exports] = parse(source);
console.log(imports)
// [
// { n: 'a', s: 18, e: 19, ss: 3, se: 20, d: -1, a: -1 },
// { n: './b', s: 38, e: 41, ss: 23, se: 42, d: -1, a: -1 }
// ]
console.log(exports)
// [ 'default', 'b' ]
console.log(source.substring(imports[0].ss, imports[0].se));
// import a from 'a'
console.log(source.slice(imports[1].s, imports[1].e));
// ./b
})();
const content = fs.readFileSync(entryFilePath, 'utf-8')
const [imports, exports] = parse(content)
if (!exports.length && !/export\s+\*\s+from/.test(content)) {
debug(`optimizing ${id} (no exports, likely commonjs)`)
return true
}
for (const { s, e } of imports) {
let i = content.slice(s, e).trim()
i = resolver.alias(i) || i
// 过滤相对路径
if (i.startsWith('.')) {
debug(`optimizing ${id} (contains relative imports)`)
return true
}
// 过滤 没在package.json中的导入(sub dependencies)
if (!deps.includes(i)) {
debug(`optimizing ${id} (imports sub dependencies)`)
return true
}
}
预构建时cmd转圈圈
GitHub - sindresorhus/ora: Elegant terminal spinner
if (!asCommand) {
// This is auto run on server start - let the user know that we are
// pre-optimizing deps
console.log(chalk.greenBright(`[vite] Optimizable dependencies detected:`))
console.log(
Object.keys(qualified)
.map((id) => chalk.yellow(id))
.join(`, `)
)
}
let spinner: Ora | undefined
const msg = asCommand
? `Pre-bundling dependencies to speed up dev server page load...`
: `Pre-bundling them to speed up dev server page load...\n` +
`(this will be run only when your dependencies have changed)`
if (process.env.DEBUG || process.env.NODE_ENV === 'test') {
console.log(msg)
} else {
spinner = require('ora')(msg + '\n').start()
}
预构建其实是执行rollup打包
// mark non-optimized deps as external
const external = deps
.filter((id) => !qualifiedDeps.includes(id))
// make sure aliased deps are external
// https://github.com/vitejs/vite-plugin-react/issues/4
.map((id) => resolver.alias(id) || id)
const bundle = await rollup.rollup({
input: qualified, // resolveQualifiedDeps方法筛选出来的需要预构建的pkg依赖
external, // pkg中qualified的反集
// treeshake: { moduleSideEffects: 'no-external' },
onwarn: onRollupWarning(spinner, options),
...rollupInputOptions,
// 复杂的是这些插件
plugins: [
createDepAssetExternalPlugin(resolver),
entryAnalysisPlugin({ root }),
...(await createBaseRollupPlugins(root, resolver, config)),
createDepAssetPlugin(resolver, root),
...pluginsOptimizer
]
})
const { output } = await bundle.generate({
...config.rollupOutputOptions,
format: 'es',
exports: 'named',
entryFileNames: '[name].js',
chunkFileNames: 'common/[name]-[hash].js'
})
spinner && spinner.stop()
把构建好的内容放在node_modules下的指定文件夹中
for (const chunk of output) {
if (chunk.type === 'chunk') {
const fileName = chunk.fileName
const filePath = path.join(cacheDir, fileName) // C:\\hemengke\\github\\vite1\\node_modules\\.vite_opt_cache\\fileName
await fs.ensureDir(path.dirname(filePath))
await fs.writeFile(filePath, chunk.code)
}
if (chunk.type === 'asset' && chunk.fileName === '_analysis.json') {
const filePath = path.join(cacheDir, chunk.fileName)
await fs.writeFile(filePath, chunk.source)
}
}
await fs.writeFile(hashPath, depHash)
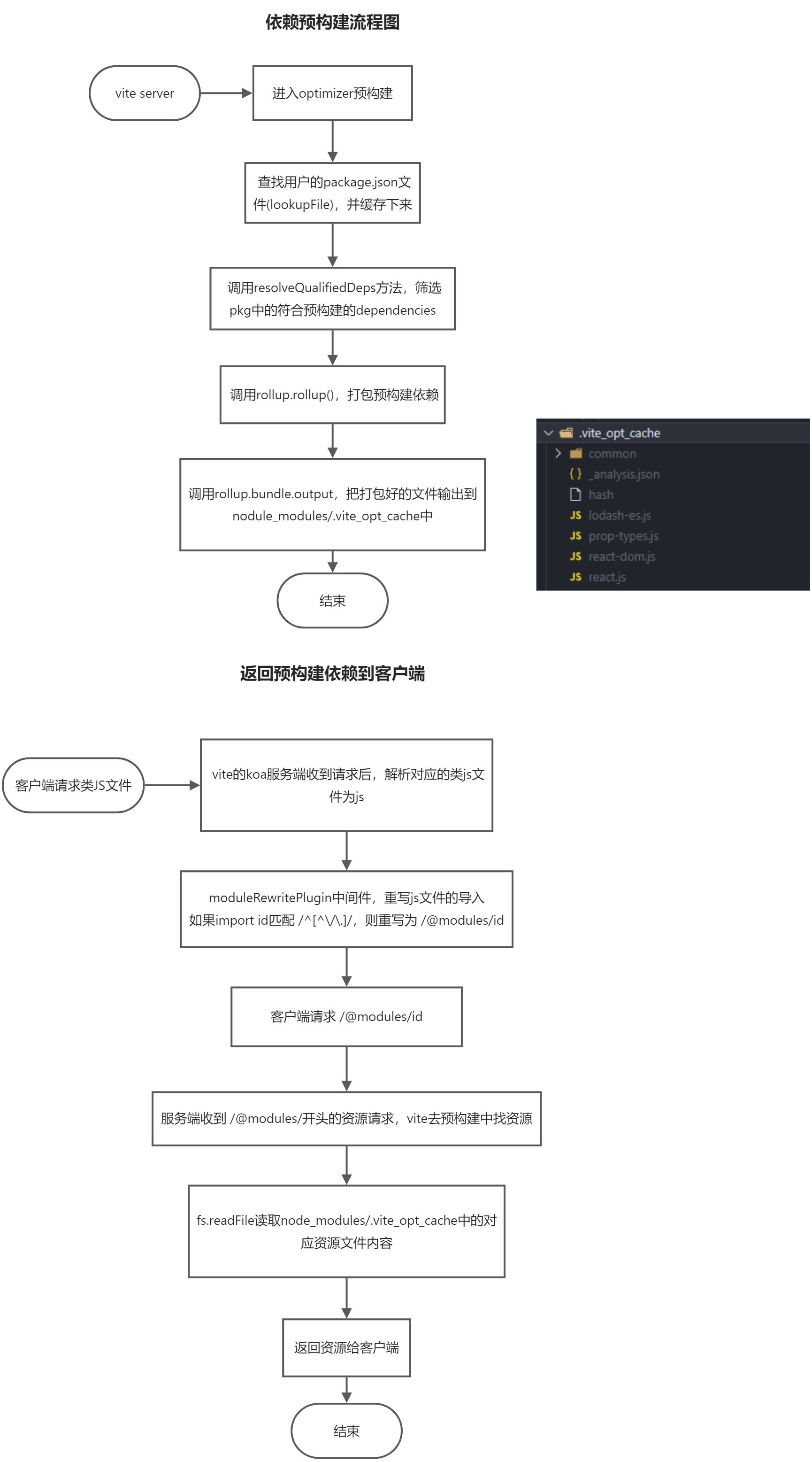
预构建好之后,vite是如何在server runtime把资源请求转发到预构建好的位置呢?
重写js文件的import moduleRewritePlugin
export const bareImportRE = /^[^\/\.]/
export const resolveImport = (
root: string,
importer: string,
id: string,
resolver: InternalResolver,
timestamp?: string
): string => {
id = resolver.alias(id) || id
// import x from 'pkg' 这种会被判定为从node_modules引入
if (bareImportRE.test(id)) {
// directly resolve bare module names to its entry path so that relative
// imports from it (including source map urls) can work correctly
// 注意:添加了 `/@modules/`, 这个会作为判断预构建的flag
id = `/@modules/${resolveBareModuleRequest(root, id, importer, resolver)}`
} else {
// 1. relative to absolute
// ./foo -> /some/path/foo
let { pathname, query } = resolver.resolveRelativeRequest(importer, id)
// 2. resolve dir index and extensions.
pathname = resolver.normalizePublicPath(pathname)
// 3. mark non-src imports
if (!query && path.extname(pathname) && !jsSrcRE.test(pathname)) {
query += `?import`
}
id = pathname + query
}
// 4. force re-fetch dirty imports by appending timestamp
if (timestamp) {
const dirtyFiles = hmrDirtyFilesMap.get(timestamp)
const cleanId = cleanUrl(id)
// only rewrite if:
if (dirtyFiles && dirtyFiles.has(cleanId)) {
// 1. this is a marked dirty file (in the import chain of the changed file)
id += `${id.includes(`?`) ? `&` : `?`}t=${timestamp}`
} else if (latestVersionsMap.has(cleanId)) {
// 2. this file was previously hot-updated and has an updated version
id += `${id.includes(`?`) ? `&` : `?`}t=${latestVersionsMap.get(cleanId)}`
}
}
return id
}
export const moduleIdToFileMap = new Map()
export const moduleFileToIdMap = new Map()
export const moduleRE = /^\/@modules\//
const getDebugPath = (root: string, p: string) => {
const relative = path.relative(root, p)
return relative.startsWith('..') ? p : relative
}
// 解析node_modules中的文件(预构建的也算其中一部分
// plugin for resolving /@modules/:id requests.
export const moduleResolvePlugin: ServerPlugin = ({ root, app, resolver }) => {
const vueResolved = resolveVue(root)
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (!moduleRE.test(ctx.path)) {
return next()
}
// 如果依赖是已 `/@modules/` 开头,则需要vite自己去加载文件内容然后返回给客户端
// path maybe contain encode chars
const id = decodeURIComponent(ctx.path.replace(moduleRE, ''))
ctx.type = 'js'
const serve = async (id: string, file: string, type: string) => {
moduleIdToFileMap.set(id, file)
moduleFileToIdMap.set(file, ctx.path)
debug(`(${type}) ${id} -> ${getDebugPath(root, file)}`)
// read是自定义的
// ctx.read = cachedRead.bind(null, ctx) src/node/server/index.ts
await ctx.read(file)
return next()
}
// special handling for vue runtime in case it's not installed
if (!vueResolved.isLocal && id in vueResolved) {
return serve(id, (vueResolved as any)[id], 'non-local vue')
}
// already resolved and cached
const cachedPath = moduleIdToFileMap.get(id)
if (cachedPath) {
return serve(id, cachedPath, 'cached')
}
// resolve from vite optimized modules
const optimized = resolveOptimizedModule(root, id)
if (optimized) {
// 如果在预构建中找到了,就返回 .vite_opt_cache 中的文件内容
return serve(id, optimized, 'optimized')
}
const referer = ctx.get('referer')
let importer: string | undefined
// this is a map file request from browser dev tool
const isMapFile = ctx.path.endsWith('.map')
if (referer) {
importer = new URL(referer).pathname
} else if (isMapFile) {
// for some reason Chrome doesn't provide referer for source map requests.
// do our best to reverse-infer the importer.
importer = ctx.path.replace(/\.map$/, '')
}
const importerFilePath = importer ? resolver.requestToFile(importer) : root
// #829 node package has sub-package(has package.json), should check it before `resolveNodeModuleFile`
const nodeModuleInfo = resolveNodeModule(root, id, resolver)
if (nodeModuleInfo) {
return serve(id, nodeModuleInfo.entryFilePath!, 'node_modules')
}
const nodeModuleFilePath = resolveNodeModuleFile(importerFilePath, id)
if (nodeModuleFilePath) {
return serve(id, nodeModuleFilePath, 'node_modules')
}
if (isMapFile && importer) {
// the resolveNodeModuleFile doesn't work with linked pkg
// our last try: infer from the dir of importer
const inferMapPath = path.join(
path.dirname(importerFilePath),
path.basename(ctx.path)
)
if (fs.existsSync(inferMapPath)) {
return serve(id, inferMapPath, 'map file in linked pkg')
}
}
console.error(
chalk.red(
`[vite] Failed to resolve module import "${id}". ` +
`(imported by ${importer || 'unknown'})`
)
)
ctx.status = 404
})
}
客户端请求的普通文件,比如 ./a.tsx,是如何处理成浏览器可识别的代码的呢?
esbuild!
import { ServerPlugin } from '.'
import {
tjsxRE,
transform,
resolveJsxOptions,
vueJsxPublicPath,
vueJsxFilePath
} from '../esbuildService'
import { readBody, cleanUrl } from '../utils'
export const esbuildPlugin: ServerPlugin = ({ app, config, resolver }) => {
const jsxConfig = resolveJsxOptions(config.jsx)
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// intercept and return vue jsx helper import
if (ctx.path === vueJsxPublicPath) {
await ctx.read(vueJsxFilePath)
}
await next()
debugger
if (
!tjsxRE.test(ctx.path) ||
!ctx.body ||
ctx.type === 'text/html' ||
resolver.isPublicRequest(ctx.path)
) {
return
}
ctx.type = 'js'
const src = await readBody(ctx.body)
const { code, map } = await transform(
src!,
resolver.requestToFile(cleanUrl(ctx.url)),
jsxConfig,
config.jsx
)
ctx.body = code
if (map) {
ctx.map = JSON.parse(map)
}
})
}
// transform used in server plugins with a more friendly API
export const transform = async (
src: string,
request: string,
options: TransformOptions = {},
jsxOption?: SharedConfig['jsx'],
exitOnFailure?: boolean
) => {
const service = await ensureService()
const file = cleanUrl(request)
options = {
loader: options.loader || (path.extname(file).slice(1) as Loader),
sourcemap: true,
// ensure source file name contains full query
sourcefile: request,
target: 'es2020',
...options
}
try {
const result = await service.transform(src, options)
if (result.warnings.length) {
console.error(`[vite] warnings while transforming ${file} with esbuild:`)
result.warnings.forEach((m) => printMessage(m, src))
}
let code = result.code
// if transpiling (j|t)sx file, inject the imports for the jsx helper and
// Fragment.
if (file.endsWith('x')) {
if (!jsxOption || jsxOption === 'vue') {
code +=
`\nimport { jsx } from '${vueJsxPublicPath}'` +
`\nimport { Fragment } from 'vue'`
}
if (jsxOption === 'preact') {
code += `\nimport { h, Fragment } from 'preact'`
}
}
return {
code,
map: result.map
}
} catch (e) {
console.error(
chalk.red(`[vite] error while transforming ${file} with esbuild:`)
)
if (e.errors) {
e.errors.forEach((m: Message) => printMessage(m, src))
} else {
console.error(e)
}
debug(`options used: `, options)
if (exitOnFailure) {
process.exit(1)
}
return {
code: '',
map: undefined
}
}
}
read response body to string
学会如何读取stream
/**
* Read already set body on a Koa context and normalize it into a string.
* Useful in post-processing middlewares.
*/
export async function readBody(
stream: Readable | Buffer | string | null
): Promise<string | null> {
if (stream instanceof Readable) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let res = ''
stream
.on('data', (chunk) => (res += chunk))
.on('error', reject)
.on('end', () => {
resolve(res)
})
})
} else {
return !stream || typeof stream === 'string' ? stream : stream.toString()
}
}
server时的中间件
一定要注意顺序啊!洋葱模型。前置(next之前的)按序执行,后置(next之后的)倒序执行
const resolvedPlugins = [
// rewrite and source map plugins take highest priority and should be run
// after all other middlewares have finished
sourceMapPlugin,
moduleRewritePlugin,
htmlRewritePlugin,
// user plugins
...toArray(configureServer),
envPlugin,
moduleResolvePlugin,
proxyPlugin,
clientPlugin,
hmrPlugin,
...(transforms.length || Object.keys(vueCustomBlockTransforms).length
? [
createServerTransformPlugin(
transforms,
vueCustomBlockTransforms,
resolver
)
]
: []),
vuePlugin,
cssPlugin,
enableEsbuild ? esbuildPlugin : null,
jsonPlugin,
assetPathPlugin,
webWorkerPlugin,
wasmPlugin,
serveStaticPlugin
]
resolvedPlugins.forEach((m) => m && m(context))
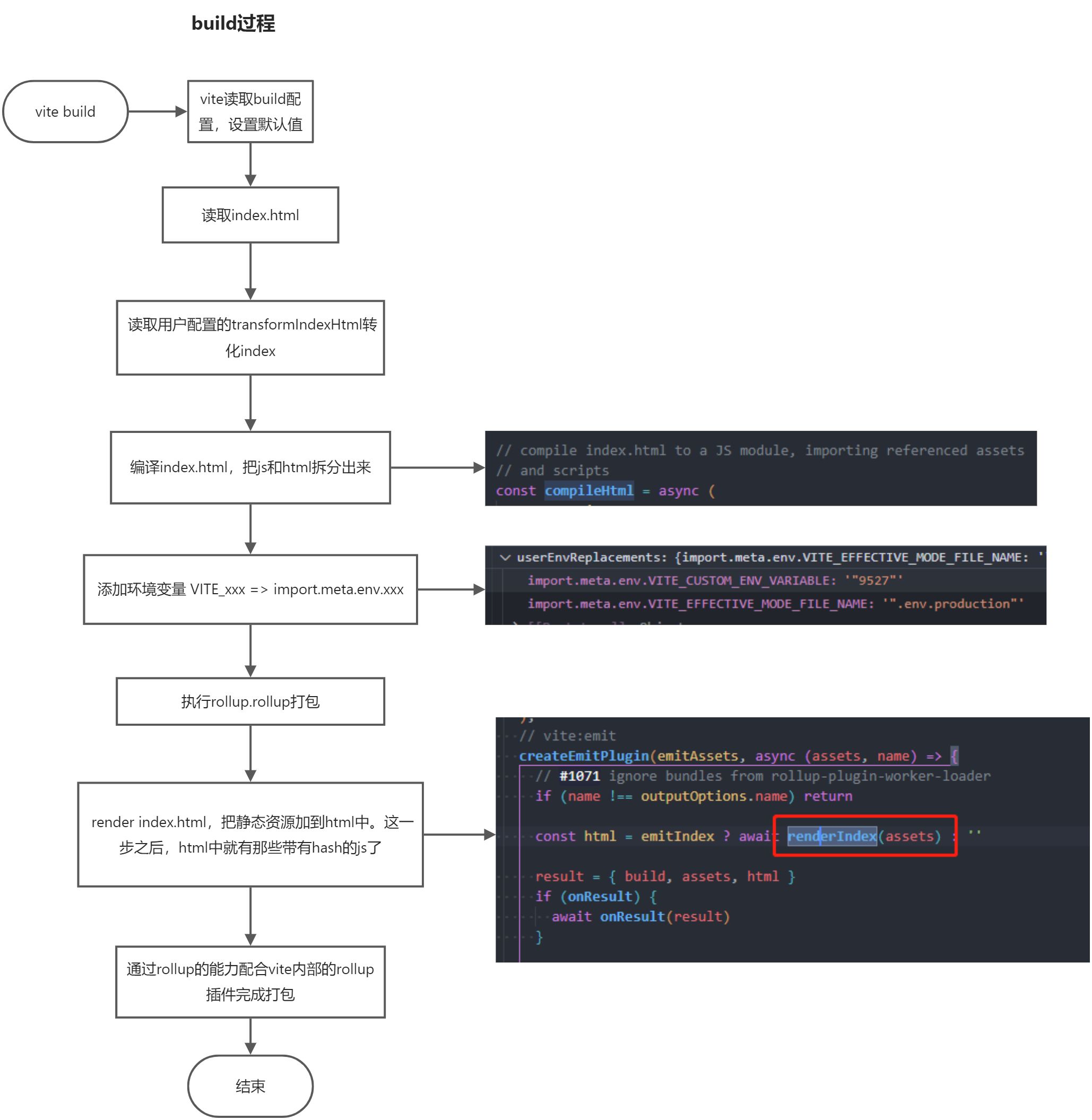
build
计算文件大小
function printFileInfo(
filePath: string,
content: string | Uint8Array,
type: WriteType
) {
const needCompression =
type === WriteType.JS || type === WriteType.CSS || type === WriteType.HTML
const compressed = needCompression
? `, brotli: ${(require('brotli-size').sync(content) / 1024).toFixed(2)}kb`
: ``
console.log(
`${chalk.gray(`[write]`)} ${writeColors[type](
path.relative(process.cwd(), filePath)
)} ${(content.length / 1024).toFixed(2)}kb${compressed}`
)
}
copy文件
// copy over /public if it exists
if (write && emitAssets && fs.existsSync(publicDir)) {
for (const file of await fs.readdir(publicDir)) {
await fs.copy(path.join(publicDir, file), path.resolve(outDir, file))
}
}
✨ vite1用到的优秀node库
| cac | 脚手架命令行工具(cli) |
|---|---|
| fs-extra | 更丰富的文件操作库 |
| ws | websocket库 |
| koa | 中间件的web服务框架 |
| slash | 把windows文件路径中的 \\\\改为 / |
| ora | cmd loading动画 |
| chalk(picocolors) | 控制台打印彩色文本 |
| chokidar | 监听文件变化 |
| magic-string | 操作string |
| source-map | 生成sourcemap |
| lru-cache | latest recently used(最近最少使用算法)缓存 |
| resolve | 解析文件路径,比原生的更强大 |
| mime-types | 获取文件的mimeType |
| klona | 深度拷贝 |
| brotli-size | 获取文件brotli压缩后的体积 |
| clean-css | 美化/压缩css |
| debug | 更好的debug |
| es-module-lexer | 获取文件的import export |
| minimist | 获取脚本命令参数 |
| open | 打开文件,可以在浏览器中打开url |
| dotenv | .env环境变量 |